Are you prepared for the regulatory changes ahead? As we look towards the future, 2024 promises to bring a wave of new laws, policies, and guidelines that will shape industries and influence business operations. Navigating through this regulatory landscape will require proactive measures and a deep understanding of potential challenges and opportunities. In this blog post, we will explore the key things that businesses need to know about the 2024 regulatory outlook, highlighting the importance of staying informed and adapting strategies to ensure compliance and success in the years to come. Here is a rundown of the expected changes.
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) in effect from this year and applicable from January 17, 2025. While proposed by the European Commission and therefore only applicable to the European Union (EU), DORA has some precedent-setting aims – among them, to bolster the cyber resilience of the financial sector through robust risk management, incident reporting protocols, oversight of third-party services, regular cyber testing, and regulatory cooperation.
By mandating stringent measures for identifying, mitigating, and responding to cyber threats, DORA seeks to ensure the continuity of essential financial services and protect consumers from potential disruptions, ultimately safeguarding financial stability in the face of evolving cyber risks.
SEC Cybersecurity Rules
The SEC’s Cybersecurity Risk Management, Strategy, Governance, and Incident Disclosure by Public Rules, effective from July 2023, mandate public-listed companies to implement robust incident management processes and disclose cybersecurity risk management details. The rules aim to enhance transparency and consistency in cybersecurity disclosures.Compliance begins with annual reports for fiscal years ending on or after December 15, 2023.
The SEC’s new rules to standardize disclosures on cybersecurity risk management, strategy, governance, and incidents by public companies was enacted under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The rules require disclosure of material cybersecurity incidents within specific time frames on Form 8-K or Form 6-K for domestic registrants and foreign private issuers respectively. Annual disclosures on cybersecurity risk management, strategy, and governance are mandated on Form 10-K or Form 20-F. The rules also require the use of Inline eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) for tagging disclosures. Compliance dates vary based on the type of disclosure, with smaller reporting companies given extended periods.
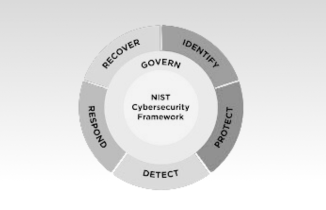
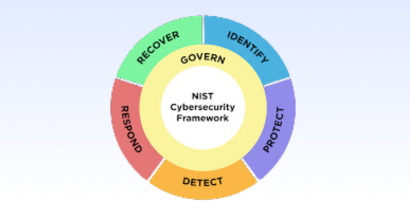
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) 2.0
The widely used National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) CSF, first published in 2014, is getting an update with Framework 2.0. This edition is designed to be accessible to all organizations regardless of their cybersecurity expertise and includes expanded core guidance and related resources to facilitate implementation. The framework emphasizes governance and aligns with the National Cybersecurity Strategy, extending its scope beyond critical infrastructure to all sectors. New resources such as implementation examples and quick-start guides cater to different types of users, while tools like the CSF 2.0 Reference Tool and Cybersecurity and Privacy Reference Tool facilitate implementation and communication.
NIST plans to continue enhancing the framework based on user feedback, with translations into multiple languages underway. Additionally, NIST collaborates with international organizations like ISO/IEC to align cybersecurity standards globally. The final version has just been released at the time of this publication.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) is currently reviewing CMMC 2.0, a comprehensive framework aimed at safeguarding sensitive unclassified information in the defense industrial base (DIB). Building upon CMMC 1.0, the upcoming version seeks to simplify compliance procedures, reduce costs, and strengthen accountability measures across the defense supply chain. Anticipated changes include streamlining compliance requirements, incorporating stakeholder feedback, and enhancing accountability mechanisms to ensure the protection of sensitive information.
By providing a more accessible and refined framework, CMMC 2.0 underscores the DoD’s commitment to bolstering cybersecurity resilience within the defense sector while fostering innovation and collaboration among stakeholders.
NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulations
The New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) released the finalized revisions to 23 NYCRR Part 500 on November 1, 2023, marking the most significant changes since its inception in 2017. The amendments, responding to evolving cybersecurity threats, aim to enhance cyber risk management for regulated entities. Notable changes include the introduction of “Class A Companies” with specific additional requirements, expanded obligations for audits, access monitoring, endpoint security, and incident response, alongside stricter enforcement measures. Covered entities must review their cybersecurity programs, assess compliance gaps, and prepare to meet new deadlines, including incident reporting by December 1, 2023, and certification submissions by April 15, 2024, with the NYDFS offering guidance and training to facilitate adherence to the updated regulations.
Data Privacy
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) amended the CCPA, introducing significant changes to privacy regulations. It grants consumers more rights, establishes the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) for enforcement, and imposes new obligations on organizations. The CPRA applies to for-profit entities meeting certain revenue or data-sharing thresholds, exempts specific categories of personal data, and introduces expanded consumer rights such as opt-out options and the right to correct inaccurate information. The CPPA enforces the CPRA, which includes penalties for intentional violations and requires businesses to implement reasonable security measures, limit data storage, and adhere to contractual obligations with third parties.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) Amendment
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) finalized an amendment to the Standards for Safeguarding Consumer Information (Safeguards Rule) under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), requiring financial institutions to report data breaches involving 500 or more consumers’ information to the FTC within thirty days of discovery. The amendment, published on November 13, 2023, will take effect on May 13, 2024. Notable changes from the original proposal include lowering the notification threshold and expanding the definition of notifiable events to include unauthorized acquisition of unencrypted customer information. Additionally, the final rule requires disclosure of whether law enforcement has determined that public notification of the breach would impede a criminal investigation or national security. These changes increase enforcement risk for affected businesses and necessitate compliance preparation to ensure adherence to the Safeguards Rule’s information security requirements.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) 4.0
PCI DSS 4.0 is the latest version of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, offering enhanced security measures for protecting payment card data. It introduces stronger encryption protocols, authentication methods, and access controls to address evolving threats in the industry while promoting a risk-based approach to security. The updated standard aims to simplify compliance requirements, streamline processes, and integrate emerging technologies like cloud computing and mobile payments securely. Overall, PCI-DSS 4.0 represents a significant advancement in safeguarding payment card data and helping organizations adapt to changing cybersecurity landscapes. It will go into effect at the end of March 2024.
Looking Ahead at the 2024 Regulatory Outlook
In conclusion, the 2024 regulatory landscape presents challenges and opportunities for businesses. It’s crucial for organizations to adopt a proactive approach, embracing innovation while ensuring ethical use of technology like AI. Cybersecurity remains paramount, demanding constant vigilance and investment in risk management. Transparency, accountability, and collaboration with regulators are key to meeting compliance requirements and fostering trust. Overall, businesses must adapt, innovate, and prioritize cybersecurity to thrive in this dynamic regulatory environment.
Juggling multiple compliance frameworks? Check out our eBook to learn how to streamline your GRC processes.