The Challenge and Importance of Kernel Development
Kernel development is a high-stakes domain where precision and expertise is paramount. A single mistake in kernel mode code can have significant repercussions, as evidenced by the recent CrowdStrike outage. This incident highlights the critical nature of kernel development and the stringent standards kernel developers must adhere to.
Developing kernel software is incredibly challenging, requiring a deep understanding of operating system internals—in this case, Windows. Kernel mode code is critical, and the dynamic interactions between your driver and the OS can lead to unforeseen issues. A single OS patch, hotfix, or update from Windows can cause your driver to crash unless all precautions are taken. Additionally, the possibility of a bug appearing within a specific build for a specific customer on a specific OS version necessitates extremely detailed and specific testing and debugging.
The Impact of a Single Developer’s Mistake
It is astonishing how one kernel developer’s error can influence not just a company’s stock but also vital sectors like healthcare and energy. The extent of the damage caused by this mistake is a stark reminder of the power and responsibility held by individual engineers. This incident underscores the immense impact that a single employee can have, even within large organizations.
Testing and Gradual Rollout: Lessons Learned
Given the scale of the disruption, the fact that CrowdStrike failed to identify the problem with its testing procedures is surprising. This raises questions about the effectiveness and thoroughness of their testing protocols and the importance of a gradual rollout of updates, utilizing control groups. Following best practices for releasing new kernel agent versions – or an agent content package – could potentially have mitigated the damage.
It is imperative to roll out the deployment gradually to different controlled groups based on different combinations of regions, OS versions, and OS hotfix/patch levels. Deploying gradually to these different groups, using validation and feedback loops before every step, ensures it is safe to proceed. This approach is key to the successful deployment of sensitive kernel updates and is also true for content or signature changes that can impact code running in kernel mode.
The Windows Agent Team’s Response
One can only imagine the tension within the Windows agent team at CrowdStrike following the incident. The moment they traced the issue back to the responsible code—likely using a `git blame`—must have been fraught with anxiety. Nevertheless, CrowdStrike acted swiftly to release and roll out a rollback update/fix, aiming to rectify the situation as promptly as possible.
Broader Implications of the Crowdstrike Outage
This outage also highlights several broader implications:
- Internal vs. External Impact: There is a significant difference between a bug that causes an internal system failure and one that brings down external systems. The latter has far-reaching consequences, affecting multiple organizations and critical services.
- Individual Responsibility: The potential impact of each engineer within a company, no matter its size, is immense. This incident serves as a powerful reminder of the responsibility that each developer carries.
Technical Breakdown: What Went Wrong
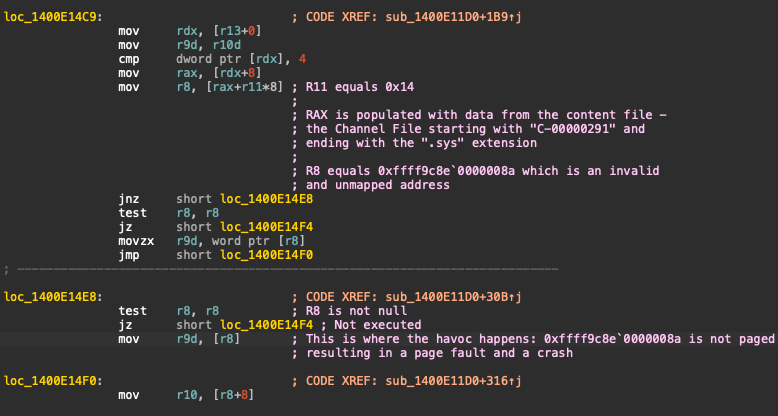
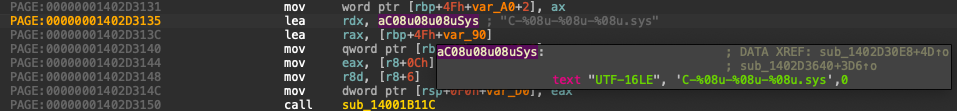
For those interested in the technical details, here is a simplistic reverse engineering of the CrowdStrike agent driver, CSAgent.sys:
- The Crashing Instruction: The instruction causing the crash (BSOD) was `mov r9d, [r8]`. In assembly language, the square brackets in the `mov` instruction indicate that the value at the address pointed to by the `r8` register should be moved to `r9d`.
- Cause of the Crash: This address was not paged, leading to a page fault and subsequently a crash, resulting in a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD). The root cause was that the `r8` register contained a garbage memory address.
- How It Happened: The `r8` register was populated with data originating from another updated file. The assembly `lea` instruction fetched the address from that file, and after additional memory computations and dereferences, it resulted in an invalid address. When the system attempted to dereference this invalid address through `r8`, it caused the crash.
Implications for Cyber GRC Programs
The CrowdStrike outage provides several key lessons for building robust Cyber Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) programs:
1. Rigorous Testing and Validation
The failure to catch the error during testing highlights the need for rigorous and comprehensive testing protocols. Cyber GRC programs must ensure that all software, especially those affecting critical systems, undergo extensive validation before deployment as part of the overall SDLC program. Implementing control groups and gradual rollouts can help identify issues before they become widespread problems.
2. Incident Response and Recovery Plans
The swift rollback update by CrowdStrike underscores the importance of having well-defined incident response and recovery plans. Cyber GRC programs should establish clear procedures for quickly addressing and mitigating the impact of software failures to minimize disruption.
This is equally crucial for organizations themselves—such as CrowdStrike’s customers—who must also have effective disaster recovery and business continuity plans. A robust plan enables organizations to recover from incidents quickly and efficiently, ensuring minimal impact on their operations.
3. Risk Assessment and Management
Understanding the potential impact of software changes on critical systems is crucial. Cyber GRC programs should incorporate thorough risk assessments into their change management processes, evaluating the possible consequences of updates and ensuring that appropriate safeguards are in place.
4. Training and Accountability
The incident emphasizes the significant responsibility of individual developers. Cyber GRC programs should invest in ongoing training for their technical teams, emphasizing best practices in secure coding and the importance of vigilance. Establishing accountability frameworks can help ensure that all team members understand the impact of their work on the broader organization.
5. Communication and Transparency
Effective communication within the organization and with stakeholders is vital during an incident. CrowdStrike’s response highlights the need for transparency in addressing issues and keeping affected parties informed. Cyber GRC programs should include communication strategies to manage stakeholder expectations and maintain trust.
Conclusion
The CrowdStrike outage serves as a poignant reminder of the critical nature of kernel development and the far-reaching consequences of errors in this domain. For Cyber GRC programs, it underscores the need for rigorous testing, robust incident response plans, thorough risk assessments, business continuity and disaster recovery planning, continuous training, and effective communication.. By integrating these lessons, organizations can enhance their resilience and better manage the complex landscape of cybersecurity risks.
As a member of the broader cybersecurity provider community, we offer our support to CrowdStrike and commend their efforts in addressing and resolving the issue swiftly. Together, we can work towards improving practices and strengthening defenses to better safeguard against future challenges.












