As we enter 2024, the convergence of challenges and opportunities within the Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) space prompts organizations to rethink their strategies. This critical juncture calls for a holistic approach that not only addresses traditional GRC concerns but also places a heightened emphasis on cybersecurity within the GRC framework. Let’s delve into the key trends shaping the GRC landscape in the upcoming year and how they intertwine with the ever-evolving cybersecurity domain.
The State of GRC in 2024
Rise of Cyber GRC: Meeting the Cybersecurity Challenge
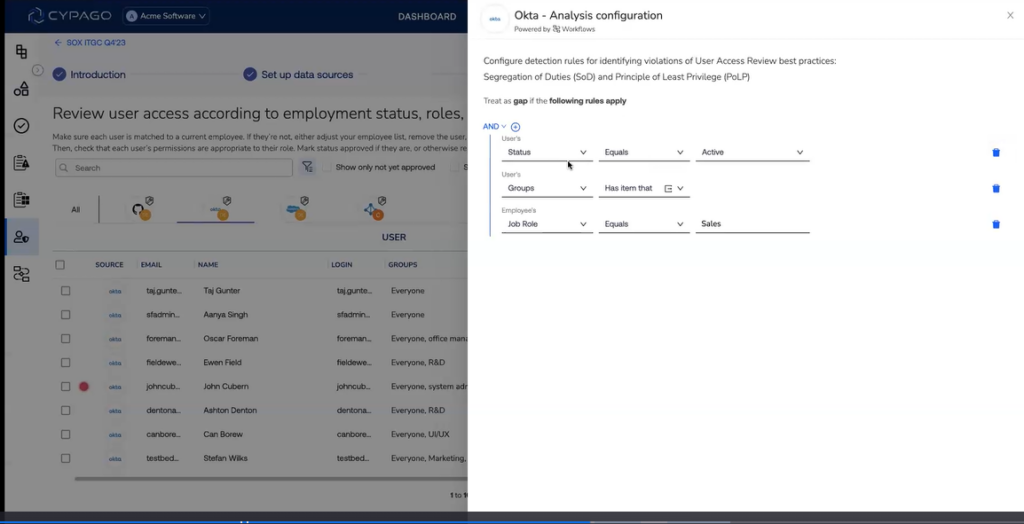
In response to the escalating frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, there is a noticeable shift towards the integration of cybersecurity within the GRC framework. Cyber GRC, a specialized branch, focuses on the governance, risk management, and compliance aspects related specifically to cybersecurity. Leaders in the GRC space are expected to pivot towards Cyber GRC in 2024, recognizing the imperative to fortify organizational resilience against digital risks.
This strategic shift allows organizations to address the unique challenges posed by the dynamic cybersecurity landscape, ensuring comprehensive governance, risk management, and compliance in the digital realm. A Cyber GRC Automation (CGA) approach provides a tailored response to the growing complexity of cyber threats, offering a strategic advantage in safeguarding digital assets.
Unified 360-Degree Visibility in Cybersecurity Strategies
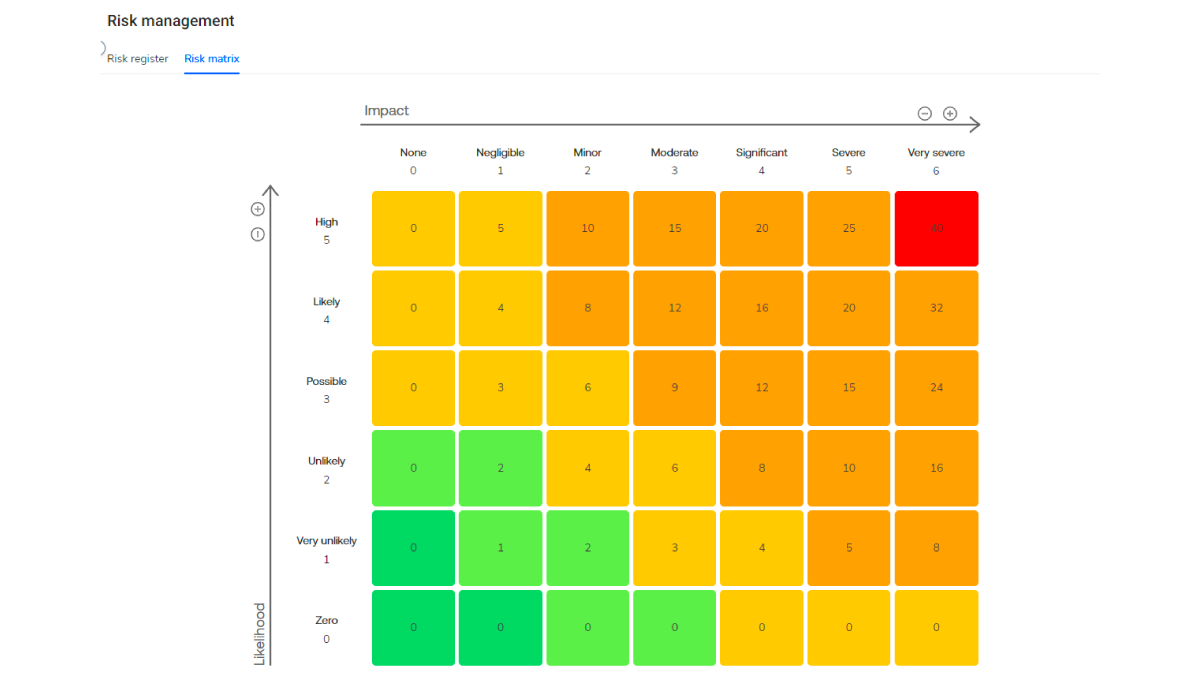
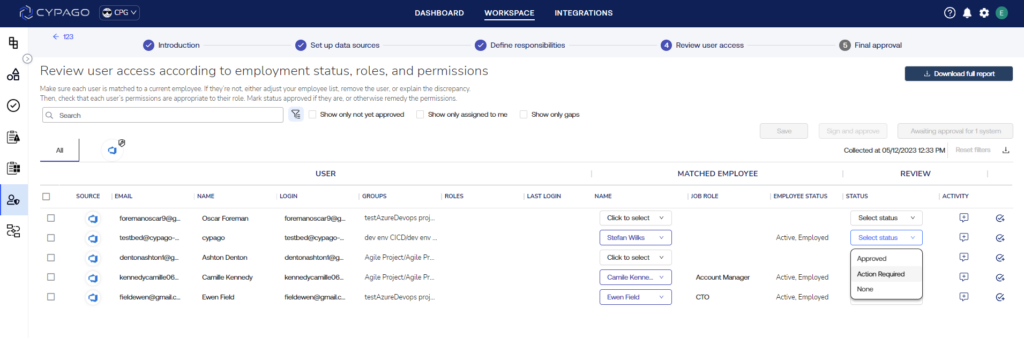
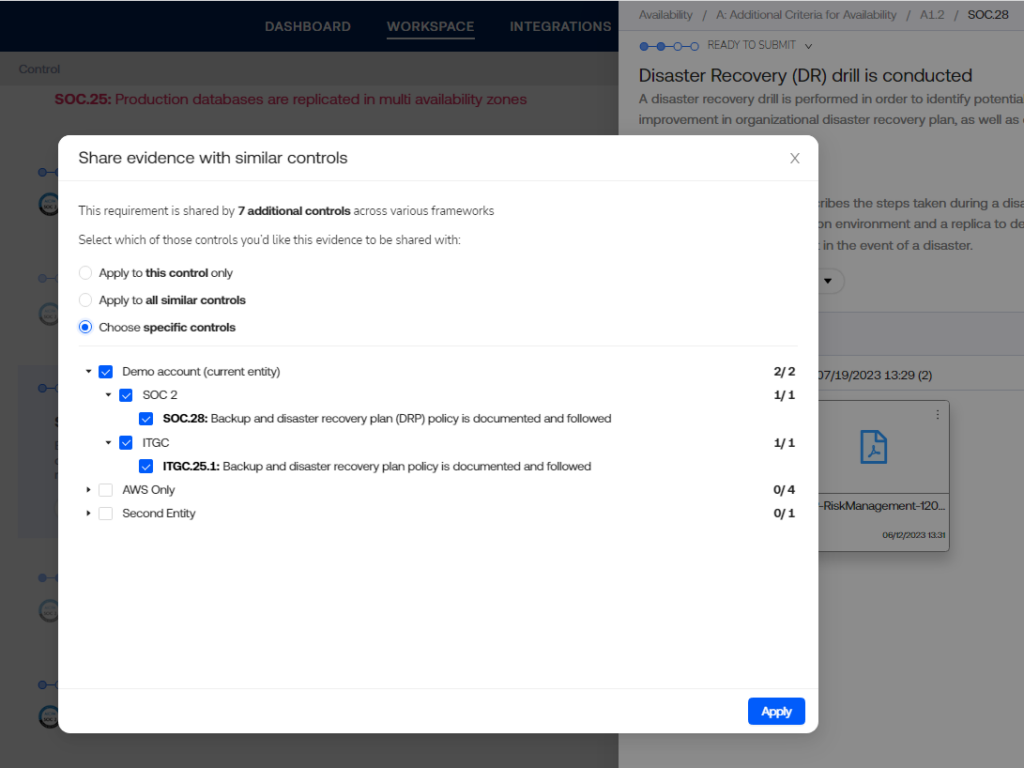
A notable trend in GRC for 2024 sees organizations reshaping their cybersecurity strategies by seamlessly integrating risks, policies, tools, data, people, processes, and technologies. This holistic approach promises a unified 360-degree visibility, enabling organizations to correlate business risks with cybersecurity programs. By creating this comprehensive view, businesses can identify and address threats with unprecedented precision, fortifying their defenses for a secure and agile digital future.
Evolving The Three Lines of Defense Model in the Digital Era
The traditional three lines of defense model, encompassing Management, Risk Management and Compliance, and Internal Audits, faces challenges in the wake of unprecedented digital transformation. While effective in various contexts, this model is increasingly strained by the expanding threat landscape of cyberattacks and data breaches. In 2024, GRC leaders must adopt a more agile approach to risk management and compliance, navigating the complexities of multiple compliance frameworks.
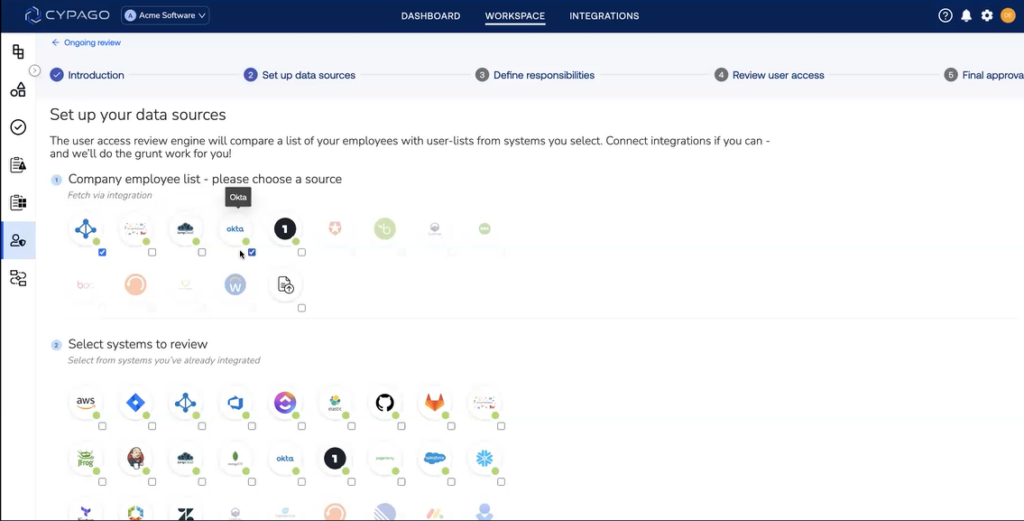
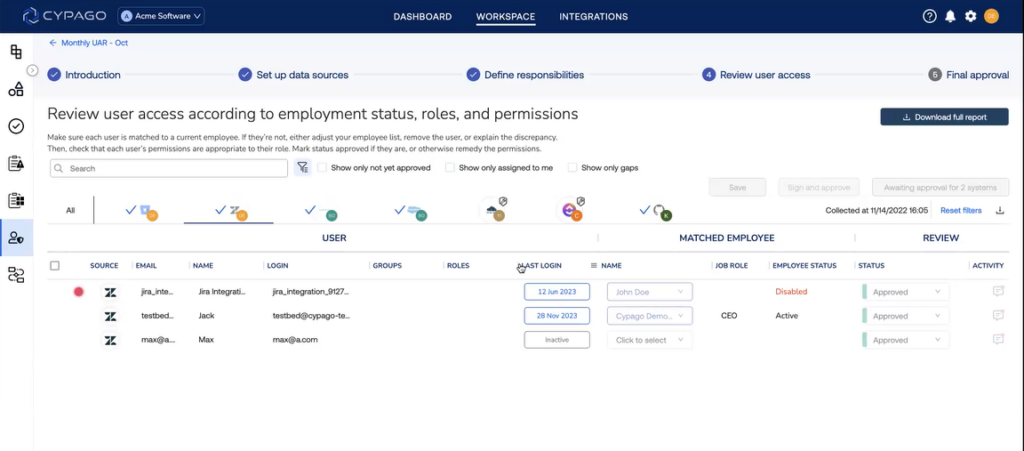
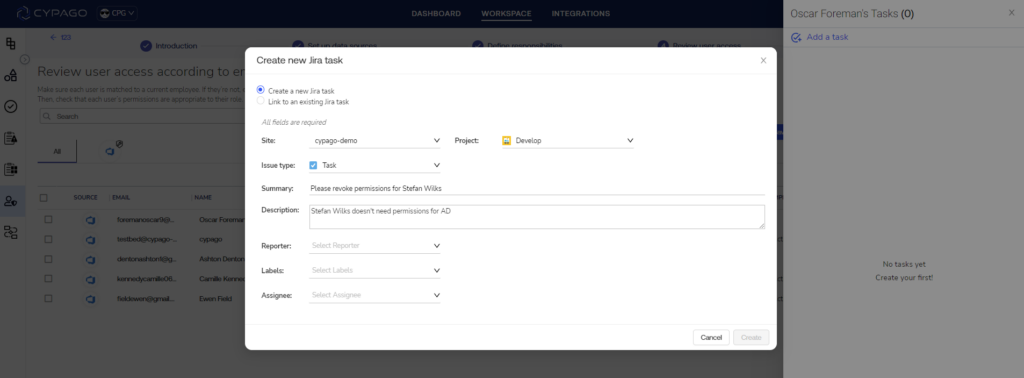
To address the growing gaps created by the changing cyber threat landscape, GRC leaders are integrating automation, advanced analytics, and real-time data intelligence. This ensures in-depth visibility across the traditional three lines of defense, fostering clearer communication with external auditors and reinforcing the organization’s ability to withstand digital risks.
AI as the Cornerstone for Remediation Guidelines
Artificial intelligence’s (AI) role in Cyber GRC in 2024 takes center stage in how GRC teams refine and enforce remediation guidelines. Organizations acknowledge AI’s pivotal role in optimizing responses, expediting reaction times, and ensuring meticulous remediation processes. The greater reliance on AI positions cyber GRC leaders to proactively address evolving cybersecurity challenges, signifying a strategic commitment to resilience and security in the digital landscape of 2024.
Ignite Your Cyber GRC Evolution with Cypago in 2024
In the crucible of 2024’s GRC landscape, the evolution of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) converges with the imperative for fortified cybersecurity – enter the era of Cyber GRC Automation. Organizations are reshaping strategies for a unified 360-degree visibility in cybersecurity, seamlessly integrating risks, policies, and technologies. Amidst transformative trends and regulatory shifts, Cypago emerges as the catalyst for this evolution, offering a dynamic suite of solutions tailored for the demands of 2024. Elevate your Cyber GRC capabilities with Cypago – your partner for resilience, agility, and success in the digitized future.
Join our webinar on Why 2024 is Year of the GRC.